For Curious Minds
Hello World!
What If You Were Born In Space?
Conceiving a baby in space is more difficult than you might think. Firstly, the absence of gravity makes it very uncomfortable for people to be intimate, and even if there is successful implantation, the problems don’t end there. Secondly, human sperm cells need gravity for migration to the egg, which makes it even more difficult for the egg to be fertilized in space. Thirdly, assuming that the fertilization is successful, it is more difficult for the embryo to mature into a baby without the proper flow of fluids from the mother’s body to the embryo.
Motion Sickness is a major problem for the healthy development of an infant. In the Zero-G environment, the fluids in our inner ear that are responsible for the perception of balance in our body just float around, causing disorientation. For children born in space, this would be especially uncomfortable when they do actually come back to Earth and experience gravity. Mice born in space have already been studied and it was observed that they had fewer problems in accustoming to weightlessness, although they had a very hard time coming to terms with orientation and balance.
Space-born babies would look a bit different. All of the fluids in our bodies are pulled downwards due to gravity, which is not possible in space. The individuals born there would develop bloated bodies and puffy faces. Since the heart doesn’t have to work against gravity in space, it would atrophy and we would loose blood content, making us paler and weaker. Due to increased blood pressure in our upper bodies, our eyes would bulge and our brains would be less efficient.
But the real question is:
 |
| Source: Google |
What Is Consciousness?
We’re still not really sure. We do know that it has to do something with different brain regions networked together rather than a single part of the brain. The thinking goes that if we figure out which bits of the brain are involved and how the neural circuitry works, we’ll figure out how consciousness emerges, something that artificial intelligence and attempts to build a brain neuron by neuron may help with. The harder, more philosophical, question is why anything should be conscious in the first place. A good suggestion is that by integrating and processing lots of information, as well as focusing and blocking out rather than reacting to the sensory inputs bombarding us, we can distinguish between what’s real and what’s not and imagine multiple future scenarios that help us adapt and survive.
 |
| Source: Google |
How Much Does A Shadow Weigh?
It looks like a silly question. You cannot take a shadow in a box with a spoon and put it on a scale. But what you can do is: weigh something with a shadow on top of it.
Do you think the weigh of an illuminated object is different than the weigh of that very same object with a shadow on top?
Well, there is.
But actually the light what weighs. Light is formed by plenty of particles called Photons.
Those photons hit the surface of objects pushing them down and making them a bit heavier. It’s like you were weighing a car while hundreds of people threw balls to the roof from a high building. It will weigh a bit more, won’t it?
You may think now… hey, but photons doesn’t have mass. And, that’s right, they don’t… but they do have energy, and at the very end, thanks to Einstein we know energy and mass are the same.
To weigh a light we will really need a very very precise good scale because light is ridiculously light.
So let’s use the only scale that is able to weigh something that light. Math.
In a sunny day, one square meter weighs approximately a nano kilogram (10−9 Kg) more than the same square meter during the night.
That’s not much… but the longer the scale the funnier the numbers.
The city of Houston weighs 180 kg more during the day than during the night just because the Sun light pushes it down.
 |
| Source: Google |
What's So Weird About Prime Numbers?
The fact you can shop safely on the internet is thanks to prime numbers – those digits that can only be divided by themselves and one. Public key encryption – the heartbeat of internet commerce – uses prime numbers to fashion keys capable of locking away your sensitive information from prying eyes. And yet, despite their fundamental importance to our everyday lives, the primes remain an enigma. An apparent pattern within them – the Riemann hypothesis – has tantalized some of the brightest minds in mathematics for centuries. However, as yet, no one has been able to tame their weirdness. Doing so might just break the internet.
 |
| Source: Google |
What Color Is A Mirror?
A mirror might look silver because it's usually depicted that way in books or movies. However, it's actually the color of whatever is reflected onto it. A perfect mirror has specular reflection, meaning it reflects all light in a single direction equal to what it receives. Specular reflection creates an image of whatever object is in front of it. But most mirrors we use aren't perfect. In fact, our mirrors reflect green light, so they often make the objects in them have a greenish tinge.
Why Do We Wear Clothes?
Clothes are something we take extremely for granted: From the moment we’re born, we’re covered in layers of fabric, and everyone around us is dressed most of the time. We have casual clothes, and formal clothes, and fashion statements – clothes are just a normal part of everyday life. You know, like democracy, cooked food and philosophy, right?
Well… Back in our species’ earliest days, we didn’t wear clothes (or have democracy, or cooked food or philosophy). We were naked. Our bits hung out. Our suitability to be part of a community wasn’t affected by what we wore. Most probably, we’d have been shunned for wearing clothes.
So why did we develop the need to wear clothes?
Evolution: As our ancestors started shedding their body hair some 170,000 years ago, they had to find an alternative way to keep warm. This, scientists assume, is the most likely reason why we started wearing clothes. In fact, outside of Africa, the Neanderthals who lived in colder climates in what would constitute modern-day Europe certainly needed some form of protection from the elements.
Modesty: Some modern-day hunter-gatherers only wear minimal clothing to cover their genitals, leading scientists to believe that at some point in our evolution we decided that certain parts of our body should not be displayed. Yet, other modern-day hunter-gatherers who wear simple clothing sometimes, also have no problem not wearing any. So that theory, while it would make sense, might not be right, anyway.
Colonization: Even today, wolverine pelts are one of the most effective things against the cold – even better than modern clothing. This has led some researchers to argue that, thousands of years ago, wearing clothes would have allowed humans to move into new habitats and lands. So, in other words, clothes helped us colonize the world.
Status & Rituals: Archaeological discoveries in the Dzudzuana Cave in Georgia have revealed that some 30,000 years ago, the modern human was already producing fabrics in various colors. At some point, it seems, clothes became more than just a necessity but part of showing off and religious rituals. This would have added a new layer of importance to garments – something that is still very true today.
What's In The Space Between Stars?
We often think of space as the absence of matter, but actual space is not really all that empty. The stars and planets are scattered throughout the galaxies, and between them is a vacuum filled with gas and dust. The gases between galaxies are often there due to a galaxy collision that rips gases away from each of the galaxies in involved. In addition, if conditions are right, supernova explosions can also drive hot gases out into intergalactic space.
How Long Does A Star Live?
Compared to humans, stars live incredibly long lives. The shortest-lived ones can shine for tens of millions of years while the old-timers can last for many billions of years. The study of stars' lives and how they are born, live, and die is called "stellar evolution", and involves looking at many types of stars to understand their life cycles.
 |
| Source: Google |
What Types Of Stars Are Out There?
Astronomers classify stars and assign "types" to them. They do this according to their temperatures and colors, along with some other characteristics. Generally speaking, there are stars like the Sun, which live their lives for billions of years before swelling up and gently dying. Other, more massive stars are called "giants" and are usually red to orange in color. There are also white dwarfs. Our Sun is properly classified as a yellow dwarf.
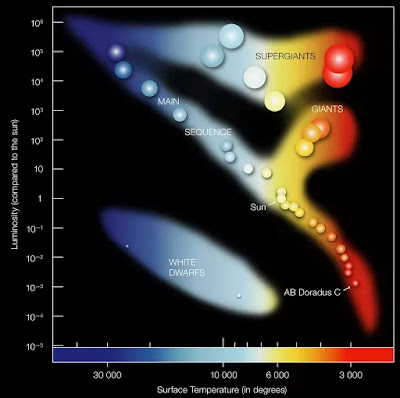 |
| Source: Google |
All in all, there are many different types of stars, ranging from tiny brown dwarfs to red and blue super-giants. There are even more bizarre kinds of stars, like neutron stars and Wolf-Rayet stars. And as our exploration of the Universe continues, we continue to learn things about stars that force us to expand on the way we think of them




Comments
Post a Comment